Targeted Drug Delivery in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Leveraging Collagen Hybridizing Peptides for Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy
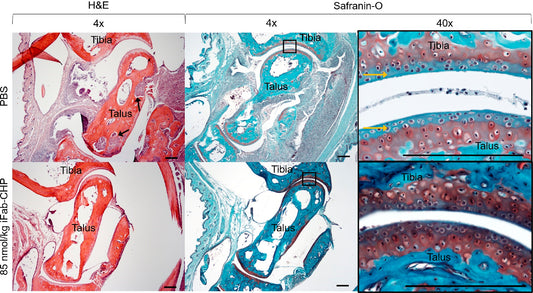
Histological staining of mouse tibia-talus joints showing healthier articular cartilage due to iFab-CHP treatment compared PBS placebo. Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease which leads to the breakdown of the cartilage in the synovial joints. Current treatment strategies with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFa) targeting neutralizing antibodies effectively reduce...
View Details
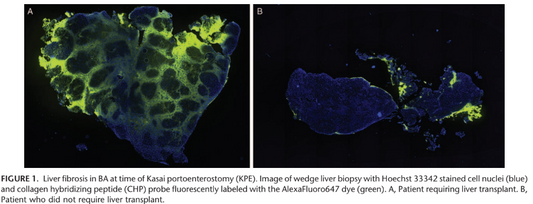
CHPs’ can Help Predict Liver Survival in Biliary Atresia
Biliary Atresia (BA) is a severe liver disease in infants, often leading to cirrhosis and death. Collagen Hybridizing Peptides (CHP) offer diagnostic and prognostic insights, aiding treatment decisions and organ transplant allocation.
View Details
Delayed Fracture Healing in Obesity-associated Type 2 Diabetic Mouse Model
Explore more about the impact of obesity-related pre-diabetic hyperglycemia on bone healing using the DIO mouse model. CHPs help reveal that deficits in collagen microstructure leads to impaired fracture healing in obese subjects.
View Details
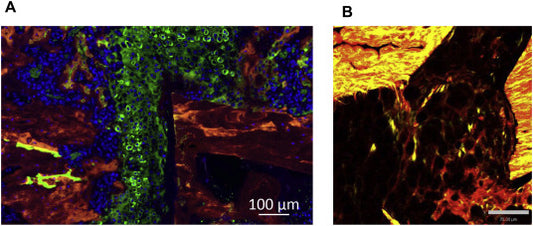
Localization of Therapeutic Fab-CHP Conjugates to Sites of Denatured Collagen for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis
In a recently accepted article published in Bioconjugate Chemistry, researchers from the University of Utah used CHPs in an antibody-conjugate to address Rheumatoid Arthritis(RA). In this paper, the authors used the Fab region from infliximab (an anti-TNFα therapy known as Remicade®) and conjugated this with CHPs. Figure Caption. A) Biodistribution of IR680 labeled bFab-(NIRF)CHP...
View Details
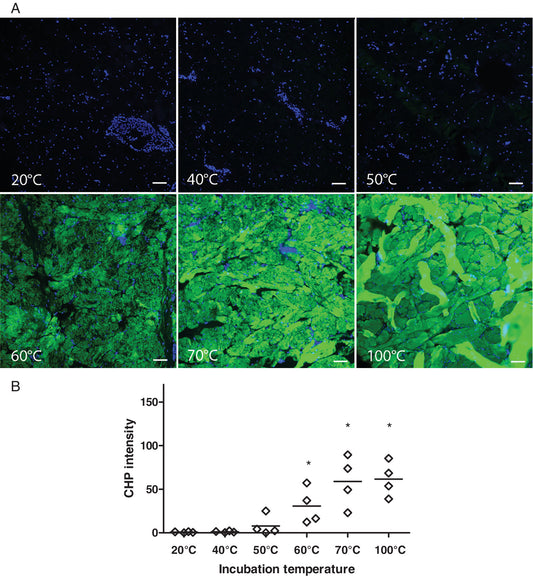
Effective enzymatic debridement of burn wounds depends on the denaturation status of collagen
Another great paper using CHPs! A recent article published in Wound Repair and Regeneration evaluated how the level of collagen denaturation within burned tissues influences the effectiveness of enzymatic debridement (removal of damaged tissue). They showed that low-temperature burns (<65 °C) had inadequate debridement, while high-temperature burns (>65 °C) had very effective debridement. By...
View Details
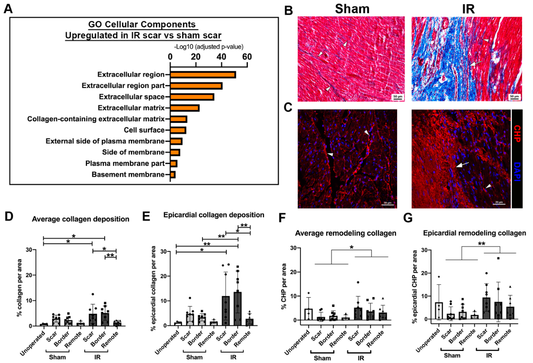
Scar Formation with Decreased Cardiac Function Following Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in 1 Month Old Swine
Learn more about how by utilizing CHPs, researchers studied post-IR pig heart damage. They found initial function decline, stable conditions later, and identified scar formation, corroborating Masson's Trichrome staining. No cardiomyocyte renewal observed.
View Details
Accumulation of collagen molecular unfolding is the mechanism of cyclic fatigue damage and failure in collagenous tissues
Discover how Jeff Weiss's team at the University of Utah innovatively use Collagen Hybridizing Peptides to unveil tendon micro-damage mechanisms, shedding light on tendon fatigue and the crucial role that collagen triple-helix unfolding has in the human body.
View Details
Intracellular Hydroxyproline Imprinting Following Resolution of Bleomycin-induced Pulmonary Fibrosis
Dr. Yong-Su Jin's research on Intracellular Hydroxyproline Imprinting explores collagen synthesis and degradation in resolving bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Using CHPs, the study challenges conventional theories, suggesting that fibrosis can self-resolve, contrary to high hydroxyproline levels imply.
View Details