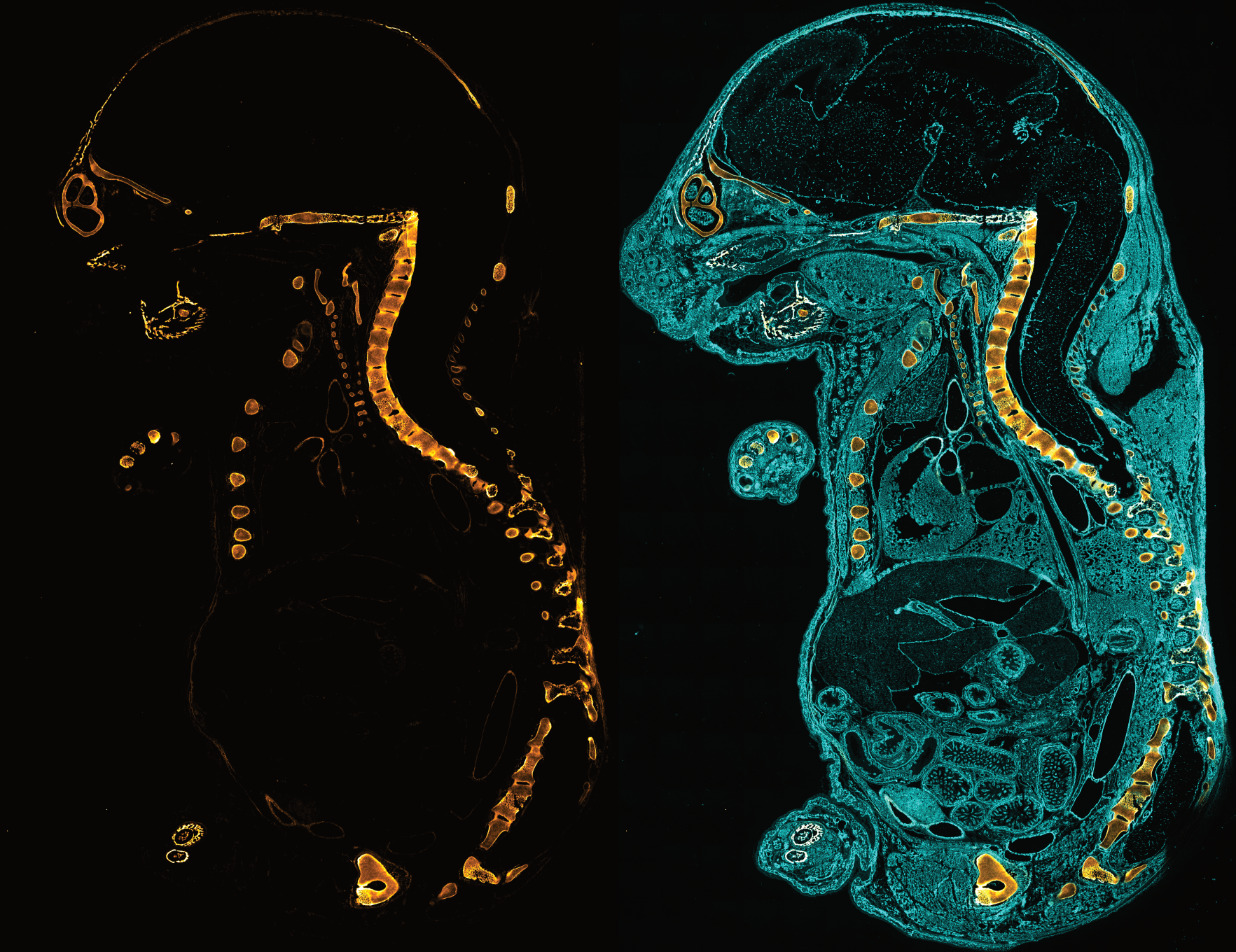
In Vivo | Collagen Hybridizing Peptides, sulfo-Cy7.5 Conjugates (sCy7.5-CHP)
SKU:
INVIVOTGT7.5
- $429.00 USD
- $429.00 USD
- Unit price
- per
Subtotal:
$429.00
User Guide with FAQ
xShipping & Returns
xOrder Processing
Please allow 1-2 Business Days to process your order. Expect an email within 2 Business Days to let you know your order is on the way!
LOCAL PICKUP - 675 S Arapeen Drive, Salt Lake City, UT 84108
Orders selected for local pickup can be picked up Monday- Friday, from 9am-4pm. An email will be sent when your order is ready for pickup.
FLAT RATE SHIPPING DOMESTIC & INTERNATIONAL
Orders are generally shipped within 1-2 Business Days using FedEx 2 Day or FedEx International Priority. Flat rate shipping fee of $39 applies to orders shipping to USA. Flat rate shipping fee of $77 applies to orders shipping WORDLWIDE. You may also opt to ‘Use Your Own FedEx Account’ at checkout and shipping will be billed directly to your account.
REFUNDS, RETURNS, AND EXCHANGES
We do not accept returns of any kind.
In the event that your order arrives damaged in any way, please email us as soon as possible at orders@3helix.com with your order number and a photo of the item’s condition. We address these on a case-by-case basis but will try our best to work towards a satisfactory solution.
If you have any further questions, please don't hesitate to contact us at orders@3helix.com.
Citations (8)
x- Huang, Kui, et al. "Targeting Molecular Collagen Defects from the Initiation of Knee Osteoarthritis." medRxiv (2024): 2024-06.
- Lab Anim (NY). 2024 Aug;53(8):196-204. doi: 10.1038/s41684-024-01408-0. Epub 2024 Jul 26.
- ACS Nano. 2021 Dec 28;15(12):19138-19149. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.1c07112. Epub 2021 Nov 5.
- J Control Release. 2023 Jan;353:278-288. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.10.017. Epub 2022 Dec 1.
- Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2023 Jun;1866(2):194928. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194928. Epub 2023 Mar 21.
- Westenskow, Peter, et al. "Use of collagen-hybridizing peptides to assess active fibrosis in 2 mouse models of choroidal neovascularization." Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science 63.7 (2022): 3870-3870.
- Ganji, Elahe. Growth and mechanobiology of the Achilles enthesis in mice. University of Delaware, 2021.
- Mol Pharm. 2017 Jun 5;14(6):1906-1915. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.7b00009. Epub 2017 May 8.
Related Products
3Helix
3Helix
3Helix
3Helix
3Helix
3Helix
3Helix
3Helix
3Helix
3Helix
Recently Viewed Products

- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.